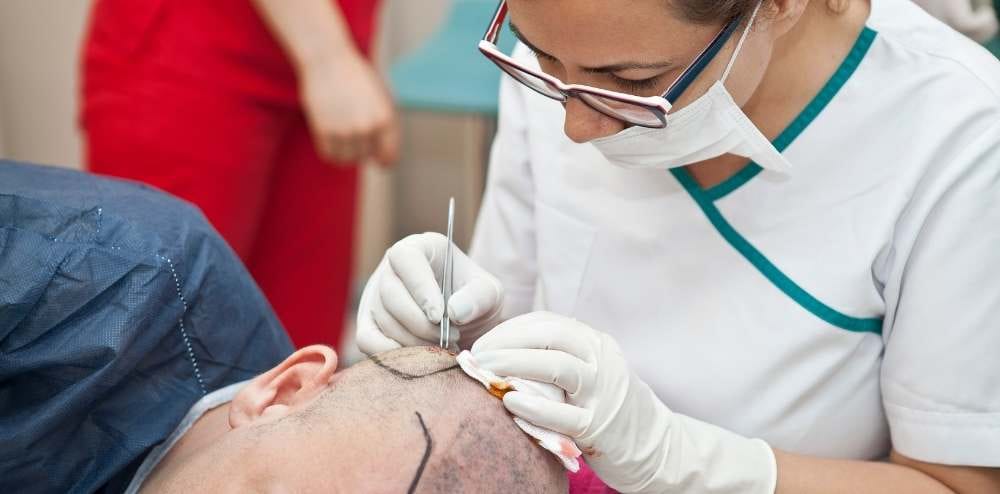
Hair transplant surgery is a common and effective way to get hair back in places on the scalp where it has been lost. But, like any surgery, hair transplant surgery comes with a small chance of problems. Folliculitis is a common problem that can come up after a hair transplant. We’ll talk about what folliculitis is, what causes it, how to spot it, and how to treat it in this blog post.
Folliculitis is what?
Folliculitis is a common skin problem that happens when hair follicles get infected or swollen. It can happen on the scalp or anywhere else on the body where hair grows. Folliculitis is usually caused by bacteria, but a virus or fungus can also cause it.
Folliculitis can cause many different signs and symptoms, such as:
- Pustules or bumps on the skin that are red, itchy, or painful.
- Skin that is swollen or hurting
- Around hair follicles, there are groups of small red bumps.
- Sores that are crusty and break open and bleed
- In extreme cases, folliculitis can cause permanent scarring or hair loss.
- Folliculitis can happen after a hair transplant.
Folliculitis can happen after any kind of surgery that removes or changes hair follicles. This includes hair transplant surgery. Most of the time, an infection is what leads to folliculitis after a hair transplant. The hair follicles on the scalp are especially likely to get sick because they are so close to each other. This makes it easy for bacteria to move from one follicle to the next.
Other things that can make folliculitis more likely after a hair transplant are:
Poor hygiene: If the scalp is not kept clean after surgery, bacteria can grow there.
Immune system problems: People with weaker immune systems are more likely to get infections, like folliculitis.
Medication: Some medicines, like immunosuppressants, can weaken the immune system and make it more likely that someone will get sick.
Allergic reactions: Some people may get folliculitis because they are allergic to the materials used during the hair transplant procedure.
How to Tell If You Have Folliculitis After Getting a Hair Transplant?
If you just had a hair transplant and have any of the following symptoms, you may have folliculitis:
- Pustules or bumps on the scalp that are red, itchy, or painful.
- Skin that is swollen or hurting
- Around hair follicles, there are groups of small red bumps.
- Sores that are crusty and break open and bleed
If you notice any of these things, you should get in touch with your hair transplant surgeon. Your surgeon can look at your scalp and tell if you have folliculitis or another type of infection.
Folliculitis needs to be treated after a hair transplant.
If you have folliculitis after a hair transplant, how you treat it will depend on how bad the infection is. Most over-the-counter medicines, like antibacterial or antifungal creams or shampoos, can be used to treat mild cases of folliculitis. Your doctor may also give you antibiotics to help the infection go away.
In cases of folliculitis that are more severe, your doctor may need to drain pus from the infected hair follicles or do a small surgery to remove the infected hair follicles. Oral steroids are sometimes given to reduce inflammation and help the body heal.Folliculitis after a hair transplant: the different kinds
After a hair transplant, there are two kinds of folliculitis that can happen: bacterial and fungal.
Bacterial Folliculitis: The most common type of folliculitis is caused by bacteria. It happens when bacteria get into the hair follicles and cause swelling and redness. The infected area usually turns red and hurts, and around the hair follicles, small pus-filled bumps may appear. Bacterial folliculitis can be caused by not taking care of your hygiene, sweating too much, or using dirty tools or equipment during a hair transplant.
Fungal folliculitis is a type of folliculitis that happens less often and can happen after a hair transplant. It is caused by a fungal infection of the hair follicles and can cause itching, redness, and small pimples around the hair follicles. People with a weak immune system or a history of skin infections are more likely to get fungal folliculitis.
Folliculitis after a hair transplant: how to treat it
If you get folliculitis after a hair transplant, you should get treatment as soon as possible to stop the infection from spreading and hurting your hair follicles even more. Folliculitis is usually treated with a mix of oral and topical antibiotics, antifungal medicine, and/or topical steroids.
Topical Antibiotics: Bacterial folliculitis is often treated with topical antibiotics. These medicines can be put on the hurt area directly to kill bacteria and reduce swelling. There are creams, ointments, and gels that can be used as antibiotics on the skin.
Oral Antibiotics: If bacterial folliculitis is very bad, oral antibiotics may be given. These medicines are taken by mouth and work from the inside out to kill bacteria. Antibiotics that are taken by mouth are usually given for a few weeks to make sure that the infection is completely gone.
Antifungal Medication: Antifungal medicine is used to treat fungal folliculitis. Depending on how bad the infection is, these medicines can be put on the skin or taken by mouth. Antifungal medicines kill the fungi and make the inflammation go away.
Topical Steroids: If you have folliculitis, you may be given topical steroids to reduce inflammation and itching. These medicines can be put on the affected area directly, and they work to reduce redness, swelling, and itching.
Folliculitis can be treated with medicine, but there are also some home remedies that can help ease the symptoms. These things are:
- Warm compress: A warm compress can help relieve itching and reduce inflammation. Soak a clean cloth in warm water and put it on the affected area for 10 to 15 minutes, two or three times a day.
- Tea tree oil: Tea tree oil can help fight an infection because it kills bacteria. Mix a few drops of tea tree oil with a carrier oil like coconut or olive oil and put it on the affected area.
- Aloe vera: Aloe vera has anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties that can help soothe the skin and lower the risk of infection. Apply fresh aloe vera gel to the area and leave it on for 20–30 minutes before washing it off.
After a hair transplant, there are some other things you can do to help deal with folliculitis:
- Keep the area clean and dry. Gently wash the area with water and a mild soap, and pat it dry with a clean towel. Don’t scratch or rub the area, as this can make the infection worse.
- Don’t use hair products on the area. Don’t use gels, hairspray, or mousse on the affected area. These products can make the infection worse by clogging the hair follicles.
- Don’t shave: Don’t shave the area until the infection has gone away completely. Shaving can make the skin red and cause the infection to spread.
- Take pain relievers. Pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen that you can buy over-the-counter can help reduce the pain and swelling caused by folliculitis.
Folliculitis after a hair transplant: how to avoid it
The best thing to do after a hair transplant is to avoid folliculitis. Here are some things you can do to lower your chance of getting folliculitis after a hair transplant:
- Keep the scalp clean: It’s important to keep the scalp clean and free of oil and dirt. Listen to what your doctor tells you about how to wash your hair after the transplant.
- Don’t touch your scalp: If you touch your scalp with dirty hands, bacteria can get into the hair follicles. Don’t touch your scalp unless you have to, and when you do, make sure your hands are clean.
- Don’t sweat: Sweat can irritate hair follicles and make them more likely to get infected. Stay away from activities that are hard on your body for at least two weeks after the transplant.
- Avoid going out in the sun. Going out in the sun can cause sunburn and make you more likely to get sick. Wear a hat or a scarf to keep the sun off your head.
- Don’t swim: Swimming exposes the scalp to bacteria in the water, which makes it more likely that you’ll get an infection. After the transplant, don’t swim for at least two weeks.
In the end,
Folliculitis can be hard and painful to deal with after a hair transplant. But it can be kept under control with the right care and preventive steps. If you think you might have folliculitis after a hair transplant, you should call your doctor right away. They’ll be able to figure out what the problem is and what the best solution is. Follow your doctor’s instructions and take steps to avoid folliculitis to make sure your hair transplant goes well and you can enjoy your new hair.